Understanding the Scope of Italian Trichology Clinics
Italian trichology clinics range from public hospital dermatology units to private centers focused on hair and scalp care. This overview explains what these clinics do, how they are organized in Italy, what to expect from assessments and treatments, and how to evaluate quality and safety before booking a consultation.
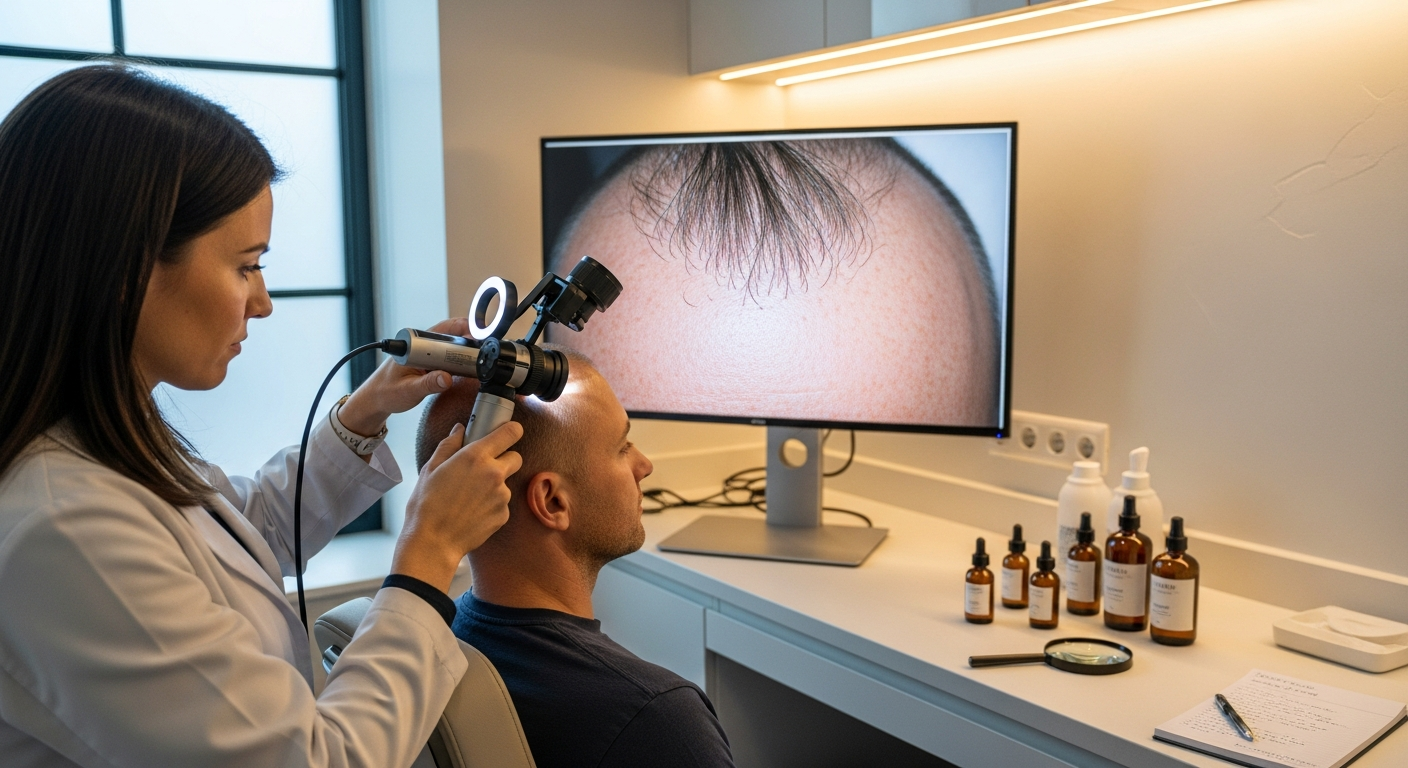
Italian trichology clinics cover a wide spectrum of services, from diagnostic evaluations in university hospitals to targeted therapies in private practices. Understanding how these clinics operate in Italy helps set realistic expectations about timelines, testing, and treatment pathways, whether you seek medical therapy, procedural options, or surgical hair restoration.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
A guide to understanding hair loss clinics
In Italy, the term “trichology clinic” can refer to dermatology-led services within public or university hospitals as well as private centers. A medically led clinic is typically run by a licensed dermatologist or plastic surgeon with training in disorders of hair and scalp. First visits usually include a clinical history (including nutrition, stress, medications, and family patterns), scalp examination, and trichoscopy (a magnified assessment of hair shafts and follicles). Depending on your presentation, physicians may request laboratory tests to rule out thyroid imbalance, iron deficiency, inflammatory markers, or autoimmune involvement. In some cases—especially suspected scarring alopecias—a small scalp biopsy may be necessary for a definitive diagnosis.
Common conditions seen in Italian clinics include androgenetic alopecia, telogen effluvium, alopecia areata, traction alopecia, and scarring conditions such as lichen planopilaris. Clinics also manage hair complaints linked to dermatologic disorders like seborrheic dermatitis or psoriasis, and they coordinate care with endocrinology, pediatrics, or gynecology when hormones or systemic illness contribute to shedding.
What is the scope of clinics in Italy?
The scope spans prevention, diagnosis, medical therapy, and procedural or surgical interventions. Medical treatments might include topical minoxidil, oral medications when appropriate and prescribed by a physician, anti-inflammatory therapies for autoimmune processes, and supportive measures such as addressing iron deficiency when present. For selected patients, clinicians may offer procedural options like intralesional corticosteroids for alopecia areata, microneedling as an adjunct, or low-level laser therapy. Some centers provide platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections; evidence is mixed and protocols vary, so clinics should explain potential benefits and limitations in clear, evidence-based terms.
Surgical hair restoration—most commonly follicular unit extraction (FUE) and, less frequently, follicular unit transplantation (FUT)—is available in specialized settings. Ethical clinics perform thorough suitability assessments, discuss donor area limitations, outline multi-stage planning when needed, and provide detailed pre- and postoperative care, including management of scalp health, realistic timelines for growth, and photographic follow-up. In public hospital pathways under the Servizio Sanitario Nazionale, access is typically via referral from a general practitioner or another specialist, and waiting times can vary by region. Private centers offer shorter scheduling but should maintain the same standards of medical evaluation and informed consent.
How to get insights on a clinic visit
When evaluating options, consider whether the service is physician-led, how diagnoses are confirmed, and what outcome measures are used. In Italy, you can verify a doctor’s registration through the Ordine dei Medici (the national medical register). Look for transparent explanations of diagnosis (with trichoscopic images when relevant), a written plan outlining treatment steps and duration, and scheduled follow-ups at defined intervals. Clinics should provide clear information on potential adverse effects, contraindications (for example, during pregnancy), and how success will be measured over time.
Practical signals of quality include standardized photography with consistent lighting, data protection compliant with GDPR, and realistic timelines (for many therapies, meaningful changes are assessed at 3–6 months, with fuller evaluation at 9–12 months). Be cautious of red flags such as guaranteed results, pressure to prepay for multi-year packages without medical justification, or transplant recommendations made without a full medical assessment. For private services, asking for an itemized plan can clarify what is included in consultations, diagnostics, procedures, and follow-up.
Representative clinics and services in Italy
Below are examples of well-known Italian institutions and their typical service scopes. This list is illustrative, not exhaustive or an endorsement.
| Provider Name | Services Offered | Key Features/Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Istituto Dermatologico San Gallicano (Rome) | Trichology consultations, trichoscopy, medical therapy, evaluation for procedural/surgical options | Research-focused IRCCS dermatology center with multidisciplinary teams |
| Humanitas Research Hospital (Rozzano, Milan) | Hair and scalp disorder clinics, dermoscopy, laboratory coordination, medical management | University-affiliated hospital with evidence-based protocols |
| Policlinico Umberto I – Sapienza University (Rome) | Dermatology outpatient trichology services, management of autoimmune and inflammatory hair disorders | Academic setting with access to advanced diagnostics |
| AOU Careggi – Dermatology (Florence) | Hair/scalp diagnostics, medical therapy, pediatric and adult trichology | Large multispecialty hospital offering integrated care |
| Policlinico S. Orsola-Malpighi – University of Bologna | Dermatology services including hair disorder assessment and follow-up | Academic expertise and collaboration across specialties |
What outcomes can you reasonably expect?
Outcomes depend on the diagnosis, disease stage, and adherence to treatment. For androgenetic alopecia, clinicians often focus on preserving existing hair and promoting density where follicles remain viable; this usually requires ongoing therapy and periodic reassessment. In telogen effluvium, addressing triggers—such as correcting iron deficiency or managing a recent stressor—can allow shedding to normalize over several months. Autoimmune conditions like alopecia areata may respond to targeted anti-inflammatory approaches; your specialist will discuss options aligned with current approvals and safety considerations. Surgical restoration changes hair distribution rather than creating new follicles, and success is linked to donor supply, technique, and postoperative care.
Building a realistic plan
An effective plan typically begins with a clear diagnosis, followed by staged interventions and scheduled reviews. Many clinics in Italy document baseline status with trichoscopic images and standardized photos, then reassess at 3–6 months. Lifestyle measures—nutrition, scalp care, and avoiding traction—complement medical treatments. Transparent communication about uncertainties, potential side effects, and alternative options helps ensure that expectations align with what medicine and surgery can objectively deliver.
In summary, the scope of Italian trichology clinics is broad and collaborative, anchored in dermatology and supported by diagnostics, medical therapies, and, when appropriate, surgical solutions. Patients who understand the clinical pathway, the role of evidence, and how to appraise provider quality are better positioned to make informed decisions and to follow a plan that matches their goals and medical needs.




