Step by Step Overview of Hair Transplantation in Germany 2025
Considering hair restoration in Germany in 2025 can feel overwhelming, with evolving techniques, strict medical standards, and many clinics to choose from. This article walks you through the process step by step, explains key options available, and highlights long term aspects to keep in mind before making a decision.
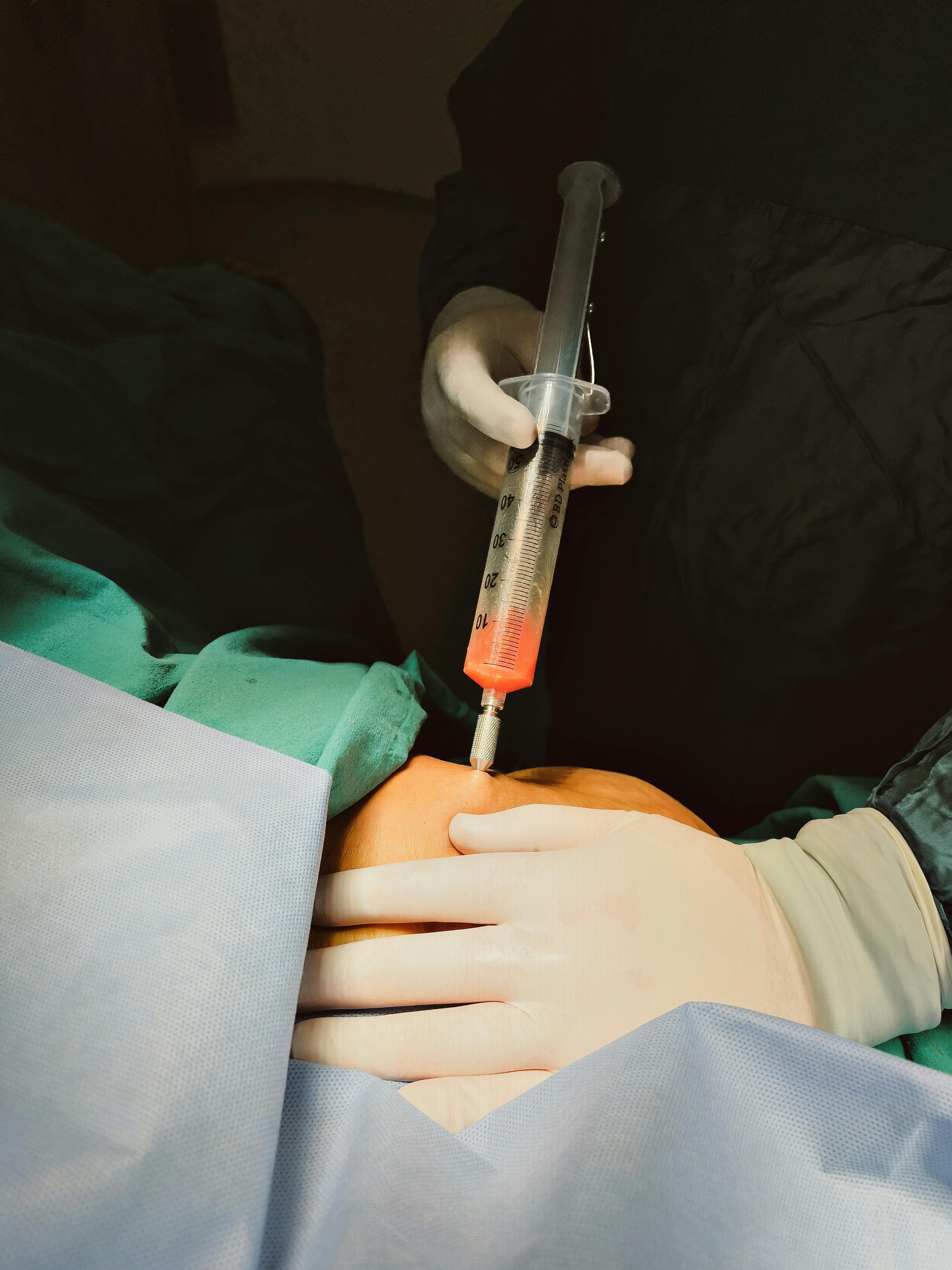
In 2025, hair transplantation in Germany combines established surgical techniques with modern diagnostics and strict medical regulation. For many people, it is not simply about appearance; it can influence confidence, social interactions, and overall well being. Understanding how the process works from the first consultation to long term follow up helps set realistic expectations and supports informed choices.
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure in which hair follicles are moved from a donor area, usually the back or sides of the scalp, to areas affected by thinning or baldness. As an informational guide to procedures, options, and long term considerations in 2025, this article focuses on the way treatments are typically planned and performed in Germany, rather than on promises of dramatic or guaranteed results.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
Step by step: How a typical procedure unfolds in Germany
The process usually begins with an initial consultation. In Germany, this is often carried out by a physician with training in dermatology or plastic surgery who evaluates the cause and pattern of hair loss, overall health, and medical history. Photographs and sometimes trichoscopy, a magnified examination of the scalp, are used to assess donor density and future hair loss risk. At this stage you discuss goals, limitations, and whether hair transplantation is appropriate or if alternative treatments are better suited.
If both patient and doctor decide to proceed, a treatment plan is created. This includes an estimate of the number of grafts to be transplanted, placement strategy for the hairline, and scheduling of the surgery day. On the day of surgery, the scalp is cleaned and local anaesthesia is administered. The donor hair is harvested from the back or sides of the head, either as a strip of skin or as individual follicular units, depending on the chosen technique. After that, tiny recipient sites are prepared in the thinning area and the follicular units are placed one by one, following the natural direction and angle of the existing hair.
What hair transplantation involves in 2025
An introduction to what hair transplantation involves and why it matters in 2025 must consider more than the surgery itself. Age, family history of hair loss, and medical conditions all influence whether a person is a suitable candidate. Hair transplantation does not stop the underlying tendency to lose hair, so further thinning in untreated areas can continue over the years. In Germany, physicians typically combine surgery with medical treatments, such as approved topical or oral medications, to stabilize or slow ongoing hair loss when possible.
Recovery after the procedure follows a predictable pattern. Mild swelling, redness, and small scabs in the transplanted area are common for several days. Many people return to desk based work within a week, but sports, swimming, and heavy physical activity are usually restricted for longer to protect grafts. Transplanted hairs frequently shed within the first month, which can be alarming if you are not prepared; visible regrowth usually begins after three to four months and continues to improve over 12 to 18 months. Long term considerations include the possibility of needing additional sessions if hair loss progresses, and the fact that scars in the donor area, although often small, are permanent.
Procedures, options, and long term considerations
In Germany, the two most widely used techniques are follicular unit transplantation, often called FUT or strip method, and follicular unit extraction, often called FUE. In FUT, a narrow strip of scalp is surgically removed from the donor region, and technicians dissect it into individual follicular units under magnification. This method leaves a linear scar that can be hidden by surrounding hair if it is kept at a certain length. FUE, in contrast, involves using tiny punches to extract individual follicular units directly from the donor area, resulting in many small dot like scars that may be less visible with short hairstyles.
Other variations, such as direct hair implantation using implanter pens, are offered by some clinics as refinements of FUE. Each option has its own profile regarding surgery length, possible scarring, and how many grafts can safely be harvested in a single session. Long term success relies on preserving donor density and planning for future hair loss. A hair transplant informational guide in 2025 must therefore emphasize conservative planning. German clinics often recommend keeping a reserve of donor hair for potential later procedures, particularly in younger patients whose final pattern of hair loss is not yet clear.
Ethical considerations also play a role. Responsible physicians avoid overly aggressive extraction that can thin the donor area or create a patchy appearance. They set realistic density targets rather than promising to recreate a teenage hairline in someone with advanced hair loss. The goal is to achieve a natural look that ages well rather than an artificially dense result that may not harmonize with future changes.
How to evaluate and choose among hair transplant options
Practical guidance on how to evaluate and choose among hair transplant options starts with understanding who is actually performing the crucial steps. In Germany, the medical framework generally requires that a licensed physician performs or closely supervises the surgery. When researching local services in your area, it is advisable to determine whether the surgeon plans the hairline design, harvests grafts, and makes the recipient sites, or whether those tasks are delegated extensively to assistants.
Experience and specialization are important. Many reputable doctors in Germany focus on a limited number of procedures, including hair transplantation, rather than offering a long list of unrelated aesthetic services. Meaningful indicators include documented before and after photographs taken under consistent conditions, clear explanations of expected outcomes, and transparent discussion of limitations and risks. Online reviews can offer impressions, but they should be interpreted cautiously and not used as the sole basis for choosing a provider.
Communication is another key factor. During consultations, a careful surgeon will ask about your priorities, explain non surgical alternatives, and point out when expectations do not match what surgery can realistically deliver. You should feel able to discuss concerns about scarring, hairstyle preferences, and the impact of ageing. Written information about aftercare, healing timelines, and follow up visits is also helpful. Since hair transplantation has permanent consequences, taking time to compare several opinions within Germany and, if needed, asking additional questions before signing a consent form can support a more measured, thoughtful decision.
In summary, hair transplantation in Germany in 2025 is a structured medical process rather than a quick cosmetic fix. From initial assessment and choice of technique to long term planning and realistic expectations, every stage benefits from clear information and careful evaluation. Understanding the steps involved, the available procedural options, and the factors that influence outcome can help prospective patients approach this permanent change to their appearance with greater confidence and clarity.




