Follicular Transplantation: Breaking Down the Medical Process
Hair loss affects millions of people worldwide, leading many to explore surgical solutions for restoring their natural hairline. Follicular transplantation represents one of the most advanced medical approaches to permanent hair restoration, utilizing sophisticated techniques to relocate healthy hair follicles from donor areas to balding or thinning regions. This comprehensive medical procedure has evolved significantly over the past decades, offering patients more natural-looking results with improved recovery times and success rates.
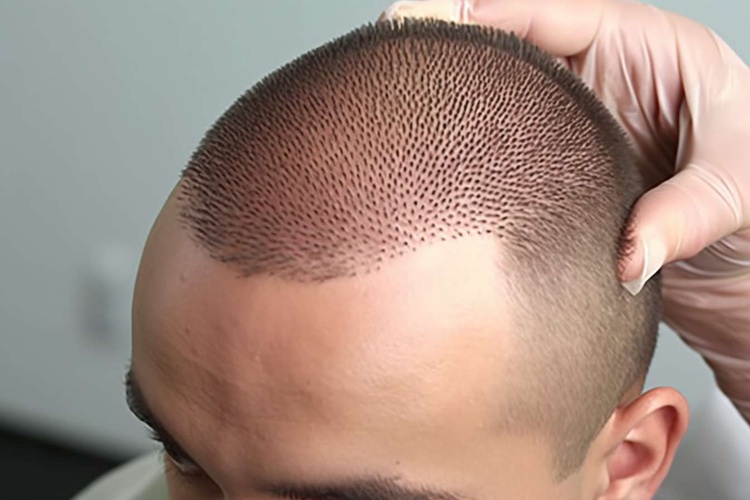
Modern hair restoration surgery has transformed from crude plug techniques of the past into refined microsurgical procedures that can produce remarkably natural results. Understanding the intricate medical process behind follicular transplantation helps patients make informed decisions about this permanent solution to hair loss.
How Hair Transplantation Works
The fundamental principle behind hair transplantation relies on the concept of donor dominance, where hair follicles from the back and sides of the scalp maintain their genetic resistance to hair loss even when moved to balding areas. During the procedure, surgeons carefully extract individual follicular units containing one to four hairs each, preserving the natural grouping patterns that create authentic-looking hair growth.
The process begins with detailed planning and hairline design, considering factors such as facial structure, age, and future hair loss patterns. Local anesthesia ensures patient comfort throughout the procedure, which can take anywhere from four to eight hours depending on the number of grafts needed.
Hair Transplant Procedures Explained
Two primary extraction methods dominate modern hair transplantation: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). FUT involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area, then dissecting it into individual follicular units under microscopic magnification. This method allows for the harvesting of large numbers of grafts in a single session.
FUE, on the other hand, involves extracting individual follicular units directly from the scalp using specialized punches ranging from 0.8 to 1.2 millimeters in diameter. This technique leaves tiny circular scars that are virtually undetectable, making it ideal for patients who prefer shorter hairstyles. The extracted follicles are then carefully implanted into recipient sites created at precise angles and depths to match natural hair growth patterns.
Hair Transplantation vs Hair Restoration Methods
While follicular transplantation represents the gold standard for permanent hair restoration, several alternative methods exist for addressing hair loss. Non-surgical options include medications like finasteride and minoxidil, which can slow hair loss and promote regrowth in some patients. Platelet-rich plasma therapy involves injecting concentrated platelets from the patient’s own blood into the scalp to stimulate hair growth.
Scalp micropigmentation creates the illusion of hair density through tattooing techniques, while hair systems and wigs offer immediate cosmetic solutions. However, surgical transplantation remains the only method that provides permanent, natural hair growth using the patient’s own follicles. The transplanted hair continues to grow normally and can be cut, styled, and treated like natural hair.
| Procedure Type | Provider Examples | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|
| FUE Hair Transplant | Bosley, Hair Club, ARTAS | $4,000-$15,000 |
| FUT Hair Transplant | Bernstein Medical, HairClub | $3,000-$12,000 |
| PRP Therapy | Local dermatologists, hair clinics | $500-$1,500 per session |
| Scalp Micropigmentation | SMP specialists, tattoo clinics | $2,000-$5,000 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Recovery and Results Timeline
The recovery process following hair transplantation involves several distinct phases. Initial healing occurs within the first week, during which patients must follow specific care instructions to protect the newly transplanted grafts. Small scabs form around each transplanted follicle, typically falling off within seven to ten days.
A phenomenon called shock loss may occur two to six weeks post-procedure, where both transplanted and existing hairs temporarily fall out due to the trauma of surgery. This is completely normal and expected. New hair growth typically begins around the third month, with significant improvement visible by six months. Final results are generally apparent twelve to eighteen months after the procedure.
Candidacy and Considerations
Not everyone is an ideal candidate for hair transplantation. Factors such as age, extent of hair loss, donor hair availability, and overall health all influence surgical candidacy. Patients with diffuse thinning patterns or insufficient donor hair may not achieve satisfactory results. Additionally, individuals with certain medical conditions or unrealistic expectations may be advised to consider alternative treatments.
The success of hair transplantation largely depends on the skill and experience of the surgical team, the quality of donor hair, and proper post-operative care. Patients should thoroughly research potential providers, review before-and-after photos, and understand both the benefits and limitations of the procedure before making a decision.
Follicular transplantation continues to evolve with advancing technology and refined techniques, offering hope to millions experiencing hair loss. While the procedure requires significant investment in both time and money, the permanent nature of results makes it an attractive option for those seeking a long-term solution to hair loss. Understanding the medical process helps patients set realistic expectations and make informed decisions about their hair restoration journey.




