Comparing FUT and FUE Surgical Methods
Hair transplant surgery has evolved significantly, offering two primary techniques that address hair loss through different approaches. Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) represent the most widely used methods in modern hair restoration. Both procedures involve relocating healthy hair follicles from donor areas to regions experiencing thinning or baldness, but they differ substantially in their extraction methods, recovery times, and overall patient experience.
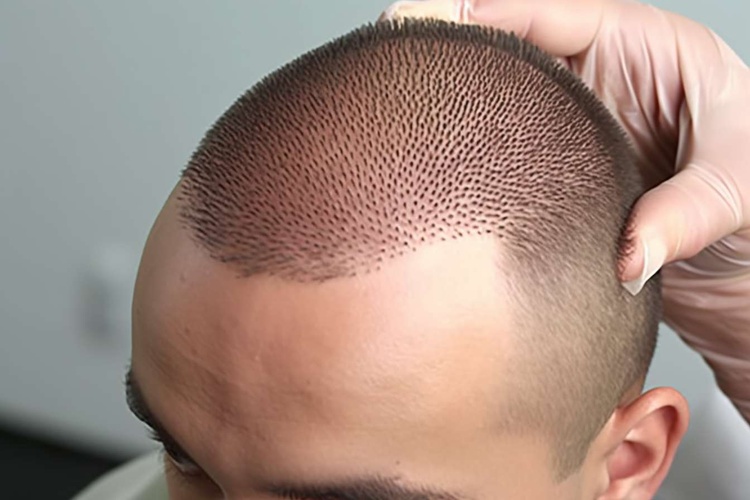
Hair loss affects millions of people worldwide, prompting many to explore surgical solutions for restoration. The field of hair transplantation has advanced considerably, with two primary techniques dominating the landscape: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). Understanding these methods helps individuals make informed decisions about their hair restoration journey.
Understanding Modern Hair Transplant Options
Both FUT and FUE procedures work by harvesting healthy hair follicles from areas of the scalp that are genetically resistant to hair loss, typically the back and sides of the head. These follicles are then carefully transplanted to areas experiencing thinning or complete hair loss. The fundamental difference lies in how the follicles are extracted from the donor area.
FUT involves removing a strip of scalp tissue from the donor area, which is then dissected under microscopes to isolate individual follicular units. FUE, on the other hand, extracts individual follicular units directly from the scalp using specialized punches, leaving tiny circular wounds that heal without visible scarring.
What To Know Before You Decide
Several factors influence the choice between FUT and FUE procedures. Patient age, hair loss pattern, donor hair density, and personal lifestyle preferences all play crucial roles in determining the most suitable approach. FUT typically allows for the transplantation of more grafts in a single session, making it ideal for patients requiring extensive coverage.
FUE offers advantages for patients who prefer shorter hairstyles or engage in activities that might put stress on a linear scar. The procedure also allows for better camouflage of the donor area immediately after surgery, as there’s no linear incision to heal.
Recovery timelines differ between the two methods. FUT patients typically experience a longer initial recovery period due to the linear incision, while FUE patients often return to normal activities sooner. However, both procedures require several months for transplanted hair to grow and show final results.
Understanding The Hair Transplant Process
The hair transplant process begins with a comprehensive consultation where surgeons evaluate the patient’s hair loss pattern, donor hair characteristics, and realistic expectations. Pre-operative planning includes designing the hairline and determining the number of grafts needed for optimal results.
During FUT procedures, surgeons carefully remove a strip of tissue, typically 1-2 centimeters wide, from the donor area. The wound is then closed with sutures or staples, leaving a linear scar that’s usually concealed by surrounding hair. The harvested tissue is processed by trained technicians who separate individual follicular units under magnification.
FUE procedures involve extracting individual follicular units using circular punches ranging from 0.8 to 1.0 millimeters in diameter. This process requires significant time and precision, as each graft must be carefully extracted to maintain its viability. The extracted follicles are then prepared for transplantation.
| Method | Provider Type | Cost Estimation | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| FUT | Hair Restoration Clinics | $4,000-$15,000 | Linear scar, higher graft yield, single session |
| FUE | Specialized Centers | $5,000-$20,000 | No linear scar, longer procedure, minimal downtime |
| Robotic FUE | Advanced Clinics | $8,000-$25,000 | Automated extraction, precision technology |
| Manual FUE | Expert Surgeons | $6,000-$18,000 | Hand-extracted grafts, customized approach |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Surgical Technique Considerations
The choice between FUT and FUE often depends on specific patient circumstances. FUT remains the preferred method for patients requiring maximum graft numbers, as it allows surgeons to harvest more follicles efficiently. The technique also provides better visualization of follicular units during extraction, potentially improving graft survival rates.
FUE suits patients who prioritize minimal scarring or those with limited donor hair density. The technique allows for selective harvesting from different areas of the donor zone, potentially preserving hair for future procedures. However, FUE typically requires multiple sessions for extensive hair loss cases.
Both procedures require skilled surgeons experienced in hair transplantation techniques. The success of either method depends heavily on proper patient selection, surgical expertise, and post-operative care. Patients should research surgeons’ credentials, view before-and-after photos, and understand realistic expectations before proceeding.
Recovery and Long-term Results
Post-operative care differs between FUT and FUE procedures. FUT patients must care for a linear incision site, avoiding activities that might stretch the wound during healing. Sutures or staples are typically removed 10-14 days after surgery. FUE patients have multiple small wounds that scab over and heal within a week.
Both procedures require patience, as transplanted hair typically sheds within 2-4 weeks before entering a resting phase. New growth usually begins around 3-4 months, with significant improvement visible by 8-12 months. Final results are typically evident 12-18 months after surgery.
Success rates for both FUT and FUE are generally high when performed by experienced surgeons. Factors affecting outcomes include patient age, hair characteristics, post-operative care compliance, and realistic expectations. Some patients may require additional procedures to achieve desired density or address continued hair loss in untreated areas.
The decision between FUT and FUE should be made in consultation with qualified hair restoration specialists who can assess individual circumstances and recommend the most appropriate approach. Both techniques have proven effective for addressing hair loss, with the choice ultimately depending on patient preferences, lifestyle factors, and specific hair restoration goals.




