Automotive Learning: Parts and Systems Guide
Modern vehicles contain thousands of interconnected parts working together to provide reliable transportation. From the engine block to the smallest sensor, each component plays a crucial role in your vehicle's performance, safety, and efficiency. This comprehensive guide explores the fundamental automotive systems and parts that every car owner should understand, helping you make informed decisions about maintenance, repairs, and upgrades while building confidence in automotive knowledge.
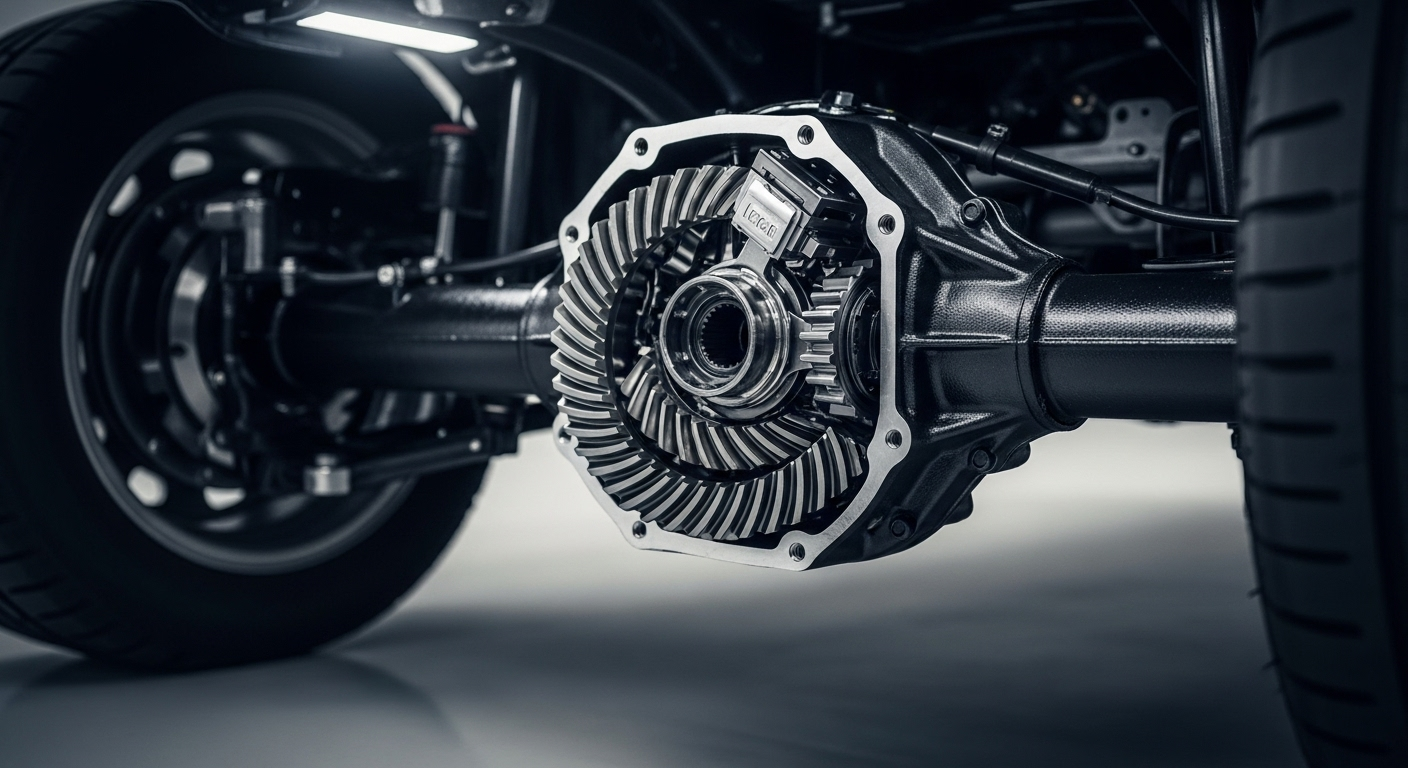
The automotive industry has evolved dramatically over the past century, transforming from simple mechanical systems to complex networks of electronic and mechanical components. Today’s vehicles integrate advanced technologies with traditional engineering principles, creating sophisticated machines that require comprehensive understanding for proper maintenance and operation.
Understanding Auto Parts: Engine Components and Their Functions
The engine serves as the heart of any vehicle, converting fuel into mechanical energy through a series of precisely timed explosions. Key engine components include the cylinder block, pistons, crankshaft, camshaft, and valvetrain assembly. The cylinder block houses the combustion chambers where fuel and air mix, while pistons move up and down to compress the mixture and transfer power to the crankshaft. The camshaft controls valve timing, ensuring proper intake of air-fuel mixture and exhaust of burned gases. Understanding these components helps drivers recognize symptoms of engine problems and communicate effectively with mechanics during service appointments.
A 2025 Educational Guide: Electrical and Electronic Systems
Modern vehicles rely heavily on electrical systems that control everything from ignition timing to entertainment features. The battery provides initial power and stores energy generated by the alternator, which converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical current. The starter motor engages the flywheel to begin engine operation, while the ignition system creates sparks at precisely the right moments. Electronic control units manage fuel injection, transmission shifting, anti-lock braking, and stability control systems. These sophisticated networks require specialized diagnostic equipment and training to service properly, making professional maintenance increasingly important.
Transmission and Drivetrain Components
The transmission system transfers power from the engine to the wheels, allowing vehicles to operate efficiently across various speeds and conditions. Manual transmissions use clutches and gear sets that drivers control directly, while automatic transmissions employ hydraulic systems and torque converters for seamless operation. The drivetrain includes components like the driveshaft, differential, and axles that distribute power to individual wheels. All-wheel drive and four-wheel drive systems add complexity with transfer cases and additional differentials, providing enhanced traction but requiring specialized maintenance procedures.
Suspension and Steering Systems
Suspension systems absorb road impacts while maintaining tire contact with the pavement, directly affecting ride comfort and vehicle control. Springs support the vehicle’s weight, while shock absorbers or struts control spring oscillation and prevent excessive bouncing. Steering systems translate driver input into wheel movement through mechanical or hydraulic assistance. Power steering pumps reduce effort required for maneuvering, while electronic power steering systems provide variable assistance based on driving conditions. Regular inspection of these components ensures safe handling and prevents premature tire wear.
Braking Systems and Safety Components
Braking systems convert kinetic energy into heat through friction, bringing vehicles to controlled stops. Disc brakes use calipers to squeeze brake pads against rotors, while drum brakes employ shoes that expand against the inner surface of brake drums. Anti-lock braking systems prevent wheel lockup during emergency stops, maintaining steering control and reducing stopping distances. Electronic stability control and traction control systems work with the braking system to prevent skids and maintain vehicle stability. These safety-critical systems require regular maintenance and immediate attention when problems arise.
| Component Category | Common Parts | Typical Service Interval | Estimated Cost Range (ZAR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engine Oil System | Oil filter, oil | 10,000-15,000 km | R300-R800 |
| Brake System | Brake pads, rotors | 40,000-80,000 km | R800-R2,500 |
| Suspension | Shock absorbers, springs | 80,000-120,000 km | R1,200-R4,000 |
| Electrical | Battery, alternator | 3-5 years | R800-R3,500 |
| Transmission | Fluid, filter | 60,000-100,000 km | R500-R1,500 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Maintenance Schedules and Best Practices
Regular maintenance prevents costly repairs and extends vehicle lifespan significantly. Manufacturer recommendations provide baseline schedules, but driving conditions in South Africa may require more frequent service intervals. Extreme temperatures, dusty conditions, and stop-and-go traffic accelerate component wear and fluid degradation. Keeping detailed maintenance records helps track service history and identify patterns that might indicate developing problems. Professional inspections can catch issues before they become expensive failures, saving money and preventing roadside breakdowns.
Understanding automotive systems empowers vehicle owners to make informed decisions about repairs, maintenance, and upgrades. While modern vehicles are increasingly complex, basic knowledge of major components and their functions helps drivers communicate effectively with service professionals and recognize when immediate attention is needed. Regular maintenance, quality parts, and professional service ensure reliable transportation and protect the significant investment that vehicles represent.




